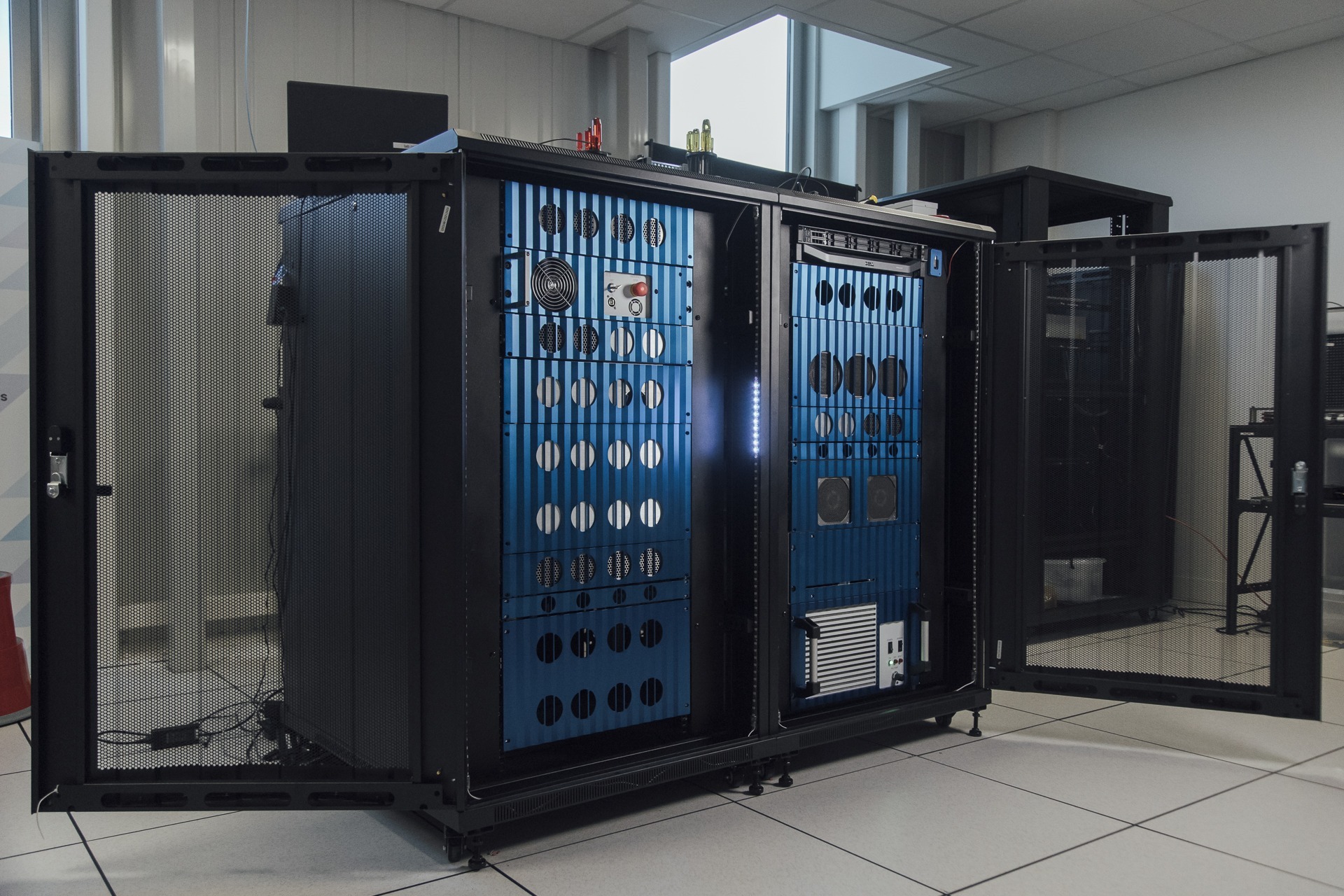
The EuroQCS-France consortium, led by GENCI and CEA, is pleased to announce that European researchers can now access a 12-qubit Quandela photonic quantum computing system remotely. This exciting development allows European users to begin programming and testing their applications on a real photonic quantum computer, months ahead of the anticipated deployment at TGCC (CEA’s computing center) of the on-premise Lucy system in the end of 2025. They can be supported by experts from a High-Level Support Team to port their applications onto the photonic quantum computer.
The EuroQCS-France consortium and the selection of Quandela as supplier by the EuroHPC Joint Undertaking (JU)
In 2024, EuroHPC JU selected a consortium formed by Quandela and its German partner attocube systems AG as the supplier of the photonic quantum computing technology as part of the EuroQCS-France initiative. This collaboration is set to pave the way for a new era in quantum computing across Europe, enhancing research capabilities and advancing the quantum ecosystem.
In November 2024, on the occasion of SC24, EuroQCS-France officially announced the provision of early remote access to a 6-qubit Quandela photonic quantum computer for the European open research community. Now, users will be able to run their code on a remote 12-qubit quantum computer, with the same design as the upcoming Lucy system. This provides a unique opportunity to engage with a photonic quantum computer, allowing open research communities to get hands-on experience before the Lucy system is fully installed and operational at TGCC in 2025.
Key Benefits for European Researchers
· Early Access: Open research communities can begin preparing their code using Perceval now, the Quandela programming and emulation environment deployed on the Joliot-Curie supercomputer, and run their applications on a remote 12-qubit photonic quantum computer similar to the targeted Lucy system.
· No Wait for Deployment: Users will not have to wait for the installation of Lucy to access a real quantum computing system, allowing them to start experimenting and testing their applications immediately.
· Expert Support: A High-Level Support Team will assist users in porting their applications onto the photonic quantum computer, ensuring that researchers can fully leverage the technology.
· Training Sessions: GENCI/CEA and Quandela will be offering specialized training on hybrid HPC-QC programming schemes, helping users prepare for the integration of Lucy with Joliot-Curie.
How to Access the Remote System
The process to access the remote Quandela system will be outlined by CEA, and interested researchers can apply for access through the designated channels. More details will be provided shortly.
Looking Ahead
EuroQCS-France is part of the broader European effort to build a diverse, pan-European hybrid HPC/QC infrastructure. Lucy, the 12-qubit photonic quantum computer, will soon join other cutting-edge quantum systems across Europe, each based on different hardware technologies. These systems include scalable superconducting qubits (Euro-Q-Exa), star-shaped superconducting qubits (LUMI-Q), trapped ions (EuroQCS-Poland), quantum annealing (EuroQCS-Spain), neutral atoms (EuroQCS-Italy), each system providing unique capabilities and research opportunities.
In the coming months, as the Lucy system’s deployment approaches, this early access will be crucial in ensuring that European researchers are well-prepared to take full advantage of the system’s capabilities.
GENCI/CEA and Quandela will be organizing training sessions on hybrid HPC-QC programming schemes leveraging photonic quantum computing to anticipate the integration of Lucy with Joliot-Curie.
About EuroQCS-France
EuroQCS-France is a consortium led by GENCI as Hosting Entity and CEA as Hosting Site, with the University Politechnica of Bucharest (UPB, Romania), Forschungszentrum Juelich (FZJ, Germany) and Irish Centre for High-End Computing (ICHEC, Ireland), selected by EuroHPC JU in 2022 as a result of the call for expression of interest EUROHPC-2022-CEI-QC-01.
EuroQCS-France aims to provide European open research communities with access to a photonic quantum computer coupled with the Joliot-Curie supercomputer, just like the 100-qubit Pasqal quantum simulator Ruby, acquired in the context of the HPCQS project.